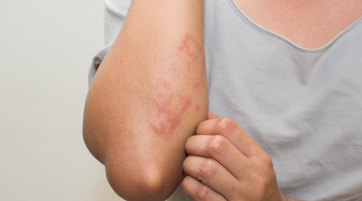
Commonly, molluscum contagiosum refers to an often-experienced ailment on the skin caused by a virus. The MCV is a member of the poxvirus family and causes it. It is a common disease among children but it may also appear in adults who have compromised immunity systems.
This article will delve into the origin of molluscum contagiosum, as well as its symptoms and possible remedies.
Causes of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is commonly spread through physical contact of an infected person or transmission of used materials such as clothes and towels.
The virus enters the body via little cuts in the skin, and usually symptoms show up after 2 to 7 weeks. Small and raised skin bumps, which are pink or flesh coloured, caused by a virus called molluscum contagiosum. Those people whose immunity is not strong (e.g. people living with HIV-AIDS), organ transplant recipients as well as those undertaking chemotherapy have a higher chance of being affected with this sickness.
Symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum gives small round fleshy colours or pink bumps on the surfaces of the skin as the main sign. Molluscum contagiosum symptoms are normally without pain but sometimes one may feel an itch especially if picked or scratched.
The dimensions are 2 – 5 mm, with a possible dimple or deep hole at the center. These molluscum contagiosum bumps tend to manifest as groups on areas like the face, neck, arms, legs and even genitalia.
Molluscum Contagiosum in Adults
Molluscum contagiosum occurs mainly among children; however, adults can be attacked by this virus too. The infection occurs mostly through sexual contact in the genitals in adults. Children often recover quickly because they can easily overcome this kind of infection, while adults have a healthier immune system thus taking a long time to recover or sometimes might not recover.
It also develops as rashes in which the areas of the skin have tiny raised bumps and lesions. The lesions may come in any colour, such as white, pink or even flesh colour. The bumps may also be itchy, get inflamed or be irritated. Adults should be treated with antivirals such as cryotherapy or curettage for molluscum contagiosum as it’s important to seek the attention of a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment of it.
Solving the Problem of Molluscum Contagiosum
Poxvirus causes mollescum contagiosum, usually a self-limiting condition that will resolve on its own without any treatment. Nonetheless, some medication could be prescribed for easing symptoms and preventing the transfer of the infection. These issues like age and location of tumour determine what kind of therapy would be appropriate for a patient. Here are some of the best ways through which you can solve Molluscum Contagiosum:
1. Wait and Watch
Sometimes, physicians advise a watch-and-wait strategy because of improvement observed with time in many instances (6-12 months). It is important not to pick or scratch these bumps during this period because they may infect other body parts with secondary bacteria.
2. Topical Medications
Some ointments and topical creams are available when treating molluscum contagiosum on the face. Such products have substances like podophyllotoxin or tretinoin that are applied on the lesions directly.
3. Cryotherapy
A healthcare provider conducts cryotherapy as a treatment of molluscum contagiosum infection. It is based on application of liquid nitrogen in an attempt to freeze bumps/lesions, thus destroying them. Cryotherapy is usually well-tolerated but may induce temporary pain or blisters in some cases.
4. Curettage
Curettage is a simple surgical technique whereby the molluscum bumps are scraped off with a little spooned device called a curette. The procedure normally takes place while under local anaesthesia, although occasional temporary scars or pigmentations occur upon the curettage procedure. It would be a good approach in removal of individual lesions.
5. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy has been proved efficient in treating molluscum contagiosum in adults. A dermatologist utilises a laser to burn the lesion in this method.
6. Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications may be prescribed in some cases such as where a patient’s molluscum contagiosum is chronic and extensive. Some medicines including Cidofovir and Imiquimod interfere with replication of viruses and also initiate the immune system.
How to Prevent it?
To prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum, it is important to follow these preventive measures:
- Stay away from direct skin-to-skin contact with infected persons.
- Avoid using your personal things like towels, clothes or razor.
- Make sure that you clean and keep the affected areas dry.
- Do not scratch or pick the boils as this will allow it to spread more and cause other infections.
- Use safe sexual behaviours to lower your chances of getting this disease via sex.
Conclusion
Lastly, molluscum contagiosum affects mostly children but may also be experienced by an adult. It spreads through direct contact or by sharing contaminated items. The features of the disease are numerous and small flesh-coloured lumps which can grow anywhere in the body.
However, the virus may clear on its own and several remedies exist for symptom relief and reduction of virus spread. Some of these alternatives are topical medications, cryotherapy, laser therapy and antiviral drugs. You need to see your doctor for appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Molluscum Contagiosum
Q2. What is the fastest way to cure Molluscum contagiosum?
The fastest way to cure molluscum contagiosum is to seek medical treatment. Options may include cryotherapy, curettage, topical medications, or laser therapy. These treatments aim to remove the lesions and help the body’s immune system clear the infection more quickly.
Q3. How serious is molluscum?
Molluscum contagiosum is generally mild and harmless, with no long-term complications. It may be more concerning for individuals with weakened immune systems, like those with HIV/AIDS or on immunosuppressive therapy.
Q4. Is molluscum contagiosum an STD?
Molluscum contagiosum is not typically considered a sexually transmitted disease (STD) in the traditional sense. It can be transmitted through sexual contact, but it can also be spread through non-sexual direct skin-to-skin contact and indirect contact with contaminated objects.